Silent Migraines: What They Are and How to Treat Them
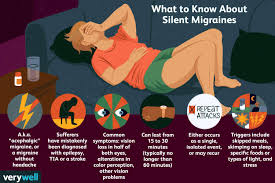
When you think of migraines, intense head pain probably comes to mind. But what if you experience all the symptoms of a migraine—nausea, visual disturbances, sensitivity to light—without the headache? This is the reality of silent migraines, also known as migraine aura without headache.
Silent migraines can be confusing and unsettling because you feel “off” but don’t have the classic migraine pain. Understanding what they are, how to recognize them, and effective treatment options can help you regain control and reduce their impact on your life.
What Are Silent Migraines?
Silent migraines involve the neurological symptoms that typically precede or accompany a migraine headache—called the aura—but without the actual headache pain.
Common symptoms include:
-
Visual disturbances like flashing lights, zigzag lines, or blind spots
-
Tingling or numbness in the face, hands, or limbs
-
Difficulty speaking or concentrating
-
Sensitivity to light or sound
-
Nausea or dizziness
Because there is no headache, silent migraines are often overlooked or misdiagnosed.
Who Gets Silent Migraines?
Silent migraines can affect anyone who experiences migraines, but they are more common in:
-
Women (migraines overall are more prevalent in females)
-
People with a family history of migraines
-
Individuals with certain neurological conditions
How Are Silent Migraines Diagnosed?
Since symptoms mimic other neurological problems like stroke or seizures, proper diagnosis is critical.
-
Your doctor will review your symptom history and perform a neurological exam.
-
Imaging tests like MRI or CT scans may be used to rule out other causes.
-
Keeping a symptom diary can help identify migraine patterns.
Treatment Options
Though silent migraines lack headache pain, they can be just as disruptive. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing attacks.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
-
Identify and avoid triggers like stress, certain foods, or hormonal changes.
-
Maintain regular sleep, hydration, and meal schedules.
-
Manage stress through mindfulness, exercise, or therapy.
2. Medications
-
Preventive medications such as beta-blockers, antidepressants, or anti-seizure drugs may reduce frequency.
-
Acute treatments like triptans can help if symptoms start to escalate.
-
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication.
3. Complementary Therapies
-
Biofeedback and relaxation techniques can reduce attack frequency.
-
Acupuncture and dietary supplements like magnesium or riboflavin may provide relief for some.
When to See a Doctor Immediately
If you experience sudden weakness, confusion, difficulty speaking, or vision loss that doesn’t resolve quickly, seek emergency care. These could signal serious conditions like stroke.
Final Thoughts
Silent migraines might fly under the radar since they lack the hallmark headache, but their impact on quality of life can be significant. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking proper diagnosis, and adopting effective treatment strategies can help you manage silent migraines and reclaim your day-to-day comfort.
Listen to your body—even when the pain is silent—and take steps toward relief.
